In Tanzania, ASSIST engaged community groups to support the work of home-based care volunteers to improve access to HIV/AIDS services and retention in care in their villages using the project’s Community Health System Strengthening model. Photo credit: URC
USAID Applying Science to Strengthen and Improve Systems (ASSIST) Project
The Challenge
Improve healthcare, strengthen health systems, and advance the frontier of improvement science in USAID-assisted countries.
Overview and Objectives
URC was the lead implementer for the USAID Applying Science to Strengthen and Improve Systems (ASSIST) cooperative agreement of the Office of Health Systems in USAID’s Global Health Bureau.
URC and its partners achieved its objectives of:
- Fostering improvements in a range of healthcare processes through the application of modern improvement methods by host-country providers and managers
- Building the capacity of host-country systems to improve the effectiveness, efficiency, client-centeredness, safety, accessibility, and equity of the healthcare services provided
- Generating new knowledge to increase the effectiveness and efficiency of applying improvement methods in low- and middle-income countries
- Strengthening maternal, newborn, and child health (MNCH) and family planning/reproductive health services in Zika-affected countries in Latin America and the Caribbean
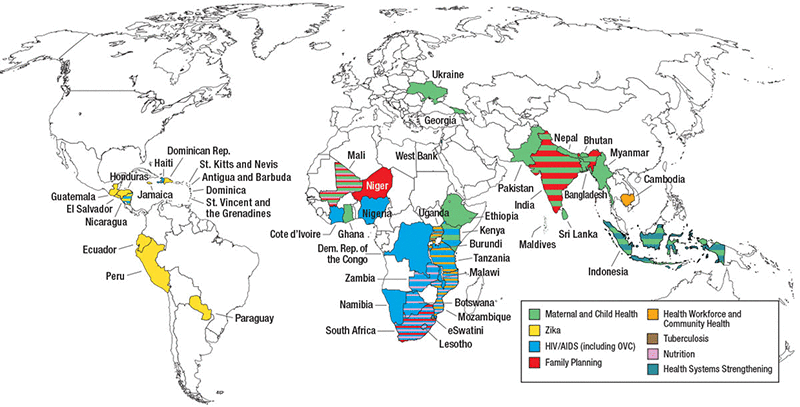
Achievements
USAID ASSIST built on the work of the USAID Health Care Improvement Project (HCI). From 2012 to 2020, USAID ASSIST operated in 46 countries, supporting quality improvement efforts for HIV and AIDS, MNCH, malaria, tuberculosis, Zika, orphans and vulnerable children, and non-communicable disease services at both facility and community levels. Refer to the Resources section below for documents that contain detailed project achievements and other related data.
The USAID ASSIST team curated a collection of 25 quality improvement resources that capture key learnings to help future projects in this space.
Video content is available on the USAID ASSIST Project YouTube channel.
News
- Blog: Where’s the Mental in World Health?
- Improving Health Care in Low- and Middle-income Countries: Collection of Case Studies
- Jamaica: From Zika Outbreak to Sustained Response
- Quality Improvement Team Approach Helps Reduce Maternal and Child Mortality in Uganda
- Zika and Beyond: Building Resiliency for Future Outbreaks
- Achieving Better Health by Improving Quality of Health Care Services in Uganda
- DREAM Big: Empowering Adolescent Girls to Stay HIV-Free
- Essential Care for Every Baby: Zika in the Caribbean
- ASSIST Project Neonatologist Shares Her Story from the Frontline Fighting Zika
- The Root Causes of Ugandans Avoiding HIV Testing and Treatment